Frequency: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
Because sound reaches our ear through the vibrating air, the speed at which the vibration travels through the air plays a major role. The speed of sound in air is 330 meters per second at room temperature. The aforementioned tone of the A4 with 440Hz therefore has a wavelength of 330 meters per second divided by 440 vibrations per second or 0.75 meters. The higher the tone, the shorter the wavelength, the lower the tone, the longer the wavelength. | Because sound reaches our ear through the vibrating air, the speed at which the vibration travels through the air plays a major role. The speed of sound in air is 330 meters per second at room temperature. The aforementioned tone of the A4 with 440Hz therefore has a wavelength of 330 meters per second divided by 440 vibrations per second or 0.75 meters. The higher the tone, the shorter the wavelength, the lower the tone, the longer the wavelength. | ||
For this reason, low-sounding instruments (large wavelengths) are always much bulkier than high (and therefore small) instruments. A loudspeaker cabinet cannot reproduce lower tones than half the wavelength, so loudspeakers for bass tones must be large. | For this reason, low-sounding instruments (large wavelengths) are always much bulkier than high (and therefore small) instruments. A loudspeaker cabinet cannot reproduce lower tones than half the wavelength, so loudspeakers for bass | ||
tones must be large. | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[octave]] | |||
[[nl:Frequentie]] | [[nl:Frequentie]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:15, 15 August 2022
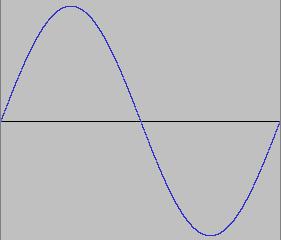
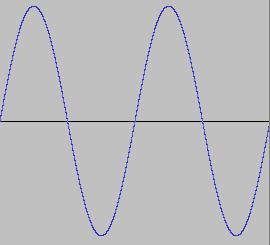
Pitch of sound is directly related to the number of vibrations per second or the frequency . The central a of the piano is tuned at 440 vibrations per second or a frequency of 440 Hertz. An octave higher has the double frequency (880 Hz), an octave lower has the half frequency or 220 Hz.
1 period, single wavelength, single frequency
2 periods, half wavelength, double frequency
Because sound reaches our ear through the vibrating air, the speed at which the vibration travels through the air plays a major role. The speed of sound in air is 330 meters per second at room temperature. The aforementioned tone of the A4 with 440Hz therefore has a wavelength of 330 meters per second divided by 440 vibrations per second or 0.75 meters. The higher the tone, the shorter the wavelength, the lower the tone, the longer the wavelength.
For this reason, low-sounding instruments (large wavelengths) are always much bulkier than high (and therefore small) instruments. A loudspeaker cabinet cannot reproduce lower tones than half the wavelength, so loudspeakers for bass tones must be large.